The Aerospace industry has been one of the most pivotal in human history, changing various aspects of our lives for the better, including materials science, propulsion, communication, and navigation systems.
The industry has evolved leaps and bounds as technologies like the Apollo Guidance Computer (AGC) put humans on the moon with 32 kilobytes of memory and a 72 kilobyte hard drive.
These technological advancements can be partially attributed in part to the implementation of aerospace software solutions.
Integrating advanced software tools has revolutionized the aerospace industry, enabling real-time monitoring, data-driven decision-making in component manufacturing, equipment management, and process optimization.
Manufacturing engineers are at the forefront of implementing process optimization software in aerospace, playing a crucial role in the industry.
They are pivotal in optimizing operations and enhancing the efficiency, quality, and safety of aircraft component manufacturing.
According to McKinsey and Co., the implementation of digitalization in the aerospace industry has allowed various manufacturing companies to achieve up to 50% less machine downtime, 30% improvements in labor productivity, 30% increases in throughput, and up to 20% decreases in the cost of quality.
Forbes also found that the digitalization of the aerospace industry has the potential to reduce development time and manufacturing costs by up to 30%.
Digitalization has moved the aerospace industry away from wind tunnel testing and into a world of CFD analysis, where manufacturing processes are continuously optimized and software that aids these optimization initiatives become game-changers.
With the importance of software solutions in the aerospace industry established, this article aims to investigate the top 4 aerospace software for manufacturing engineers in the aerospace industry.
To ensure the list of the top 4 aerospace software for manufacturing engineers is accurate and reflects the applicability of the software, the factors below were considered. These factors address common functional requirements within the Aerospace industry by manufacturing engineers.
Factors considered
1. Comprehensive data integration and real-time monitoring:
Aerospace manufacturing software should be able to seamlessly integrate with various data sources and provide real-time monitoring of processes.
Data sources can include sensor networks, historical maintenance records, Excel files, and external data feeds.
The integration of various data sources enables real-time monitoring, allowing engineers to track the health and performance of assets for immediate intervention if anomalies in the manufacturing process are detected.
2. Simulation and manufacturing analytics:
Aerospace software should allow manufacturing engineers to simulate their plant processes or equipment performance.
Simulation and process analytics allow engineers and plant operators to aggregate, visualize, and analyze real-time manufacturing data.
This functionality allows the investigation and implementation of optimization initiatives.
3. Predictive analytics:
Predictive analytics, driven by advanced analytics and machine learning (ML), allows the detection of anomalies and decreases unplanned equipment and process downtime.
Through predictive analytics, effective predictive maintenance strategies can be created and implemented leading to increased equipment availability and increased production efficiency.
4. Asset management:
Effective asset management leads to better equipment performance, less downtime, and increased equipment lifetimes.
Through historical data analysis, asset management strategies also improve utility consumption, decreasing manufacturing costs.
5. Compliance, security, and regulatory support:
Compliance, security, and regulatory support ensure that a manufacturing operation adheres to industry regulations and standards such as AS 9100 – a specific set of guidelines for implementing a quality management system for use by aviation, space, and defense organizations.
To ensure adherence to industry regulations, documentation and reporting initiatives must be backed by accurate and updated data.
Easy access to data enables reporting initiatives promoting better auditability and performance reporting.
The above criteria ensure that aerospace software adds value to aerospace manufacturing operations and addresses common initiatives.
Below we discuss the top 4 aerospace software manufacturing engineers can implement in the Aerospace industry.
1. Basetwo
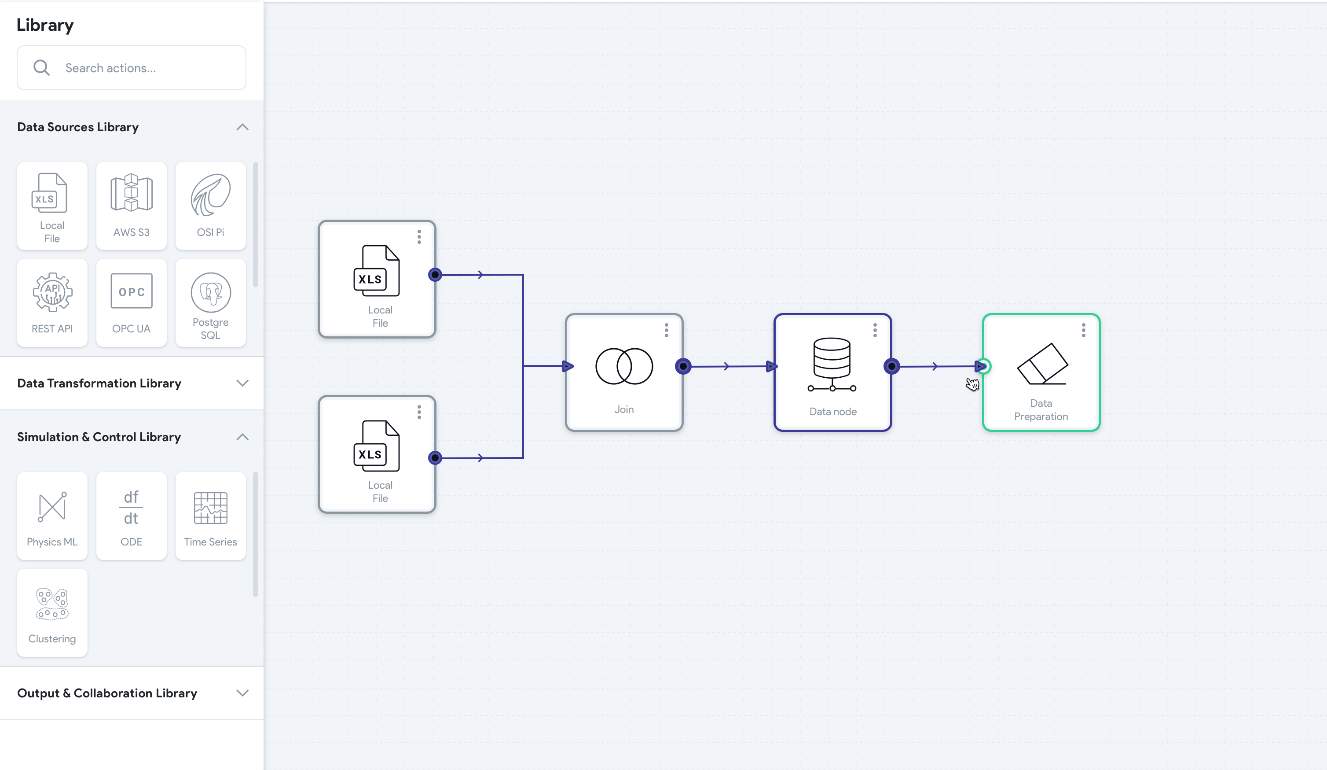
Basetwo is an AI copilot for manufacturing engineers.
The platform unifies data pipelining, model simulation, optimization, and quality control within an integrated, sophisticated, and low-code AI platform.
Basetwo allows easy data integration with both offline and online data sources and can integrate with ERP, MES, SCADA, or DCS systems; Historians such as OSIsoft; and various other data sources.
Basetwo also allows for data cleaning, modeling, and verification through a simple drag-and-drop interface and allows for optimization initiatives such as “what-if” analysis.
With its advanced simulation and modeling capabilities, Basetwo helps aerospace companies optimize manufacturing control setpoints and assembly line balancing; streamline asset maintenance schedules, and optimize service life and utilization of critical equipment.
It also allows the simulation and identification of process conditions vs product material properties to ensure design and quality specifications are met.
The cloud computing capabilities of Basetwo further allow easy access to accurate data, ensuring all reporting initiatives are backed by the most recent and precise data available.
Features:
- Drag-and-drop interface for advanced process control, optimization, virtual experimentation for aerospace products, model verification, and "what-if" analysis.
- Seamless data integration with DCS systems, OSIsoft, Excel, and various other data sources.
- Cloud-based real-time simulation and optimization for immediate decision-making support.
- Powerful process analytics that support optimization initiatives.
- Comprehensive pre-production validation for model reliability.
Basetwo Benefits:
- Digital twin creation for entire product lifecycles.
- Demonstrated experience within the aerospace sector with partners such as Boeing.
- Supports complex physics-based systems such as additive manufacturing or composite fabrication by leveraging hybrid modeling.
- A user-centric platform for engineers that prioritizes usability, catering to professionals with varying expertise.
- A collaborative environment with a templated model library facilitating teamwork and knowledge sharing with pre-designed models for aerospace products.
- Real-time simulation with cloud computing enables informed decision-making and provides immediate insights for swift adjustments and improvements for a high-risk industry such as aerospace.
- Low OEM dependence with a high degree of customization to cater to the specific needs of the aerospace sector.
Things to keep in mind:
The Basetwo platform is a powerful addition to the toolbox of manufacturing engineers working in aerospace manufacturing industries. It is however not focused on computer-aided design (CAD).
Basetwo is primarily tailored towards aerospace manufacturing and MRO process optimization, providing AI-generated recommendations enabling further cost-savings, and the identification and implementation of ideal manufacturing conditions.
Primarily focused on process and supply chain optimization with limited features for process design.

2. Siemens Opcenter for Aerospace
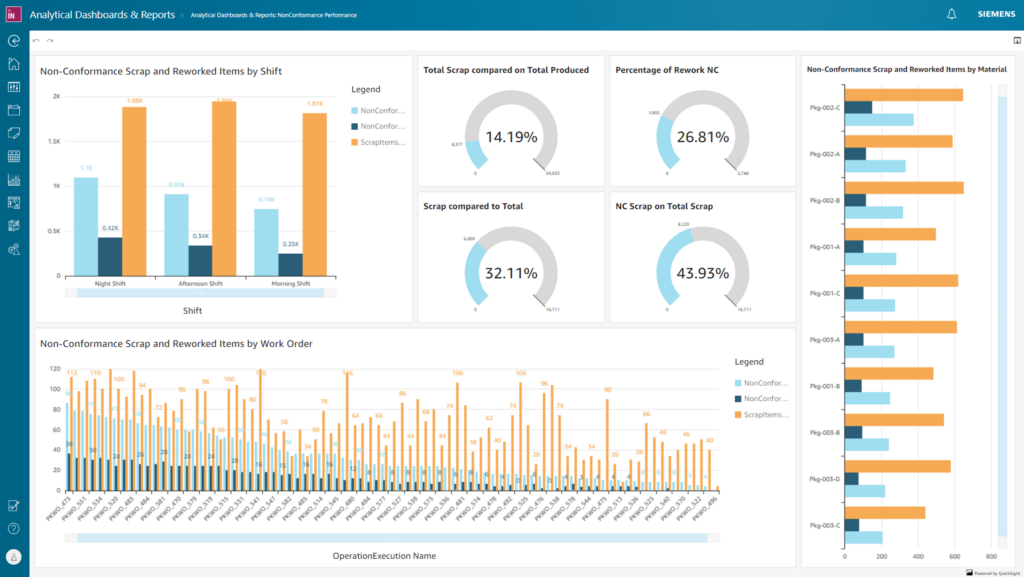
Siemens Opcenter for Aerospace is a unified manufacturing operations management (MOM) software portfolio that enables digital software operations management. It is designed to help manufacturers continuously visualize and understand their production processes, receive KPIs and high level metrics on their production performance, as well as identify areas for improvement.
The software can integrate with various data sources including Excel, SCADA, and current ERP systems. It also allows real-time monitoring.
Siemens Opcenter provides Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) that accurately captures design, engineering, and process data in the production of finished products.
It also provides customizable production planning and scheduling tools to optimize resource utilization, reduce inventory, and improve on-time delivery.
Features:
- Holistic suite encompassing real-time monitoring and descriptive analytics
- Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) capabilities
- Smart Virtual Sensing framework to support analytics.
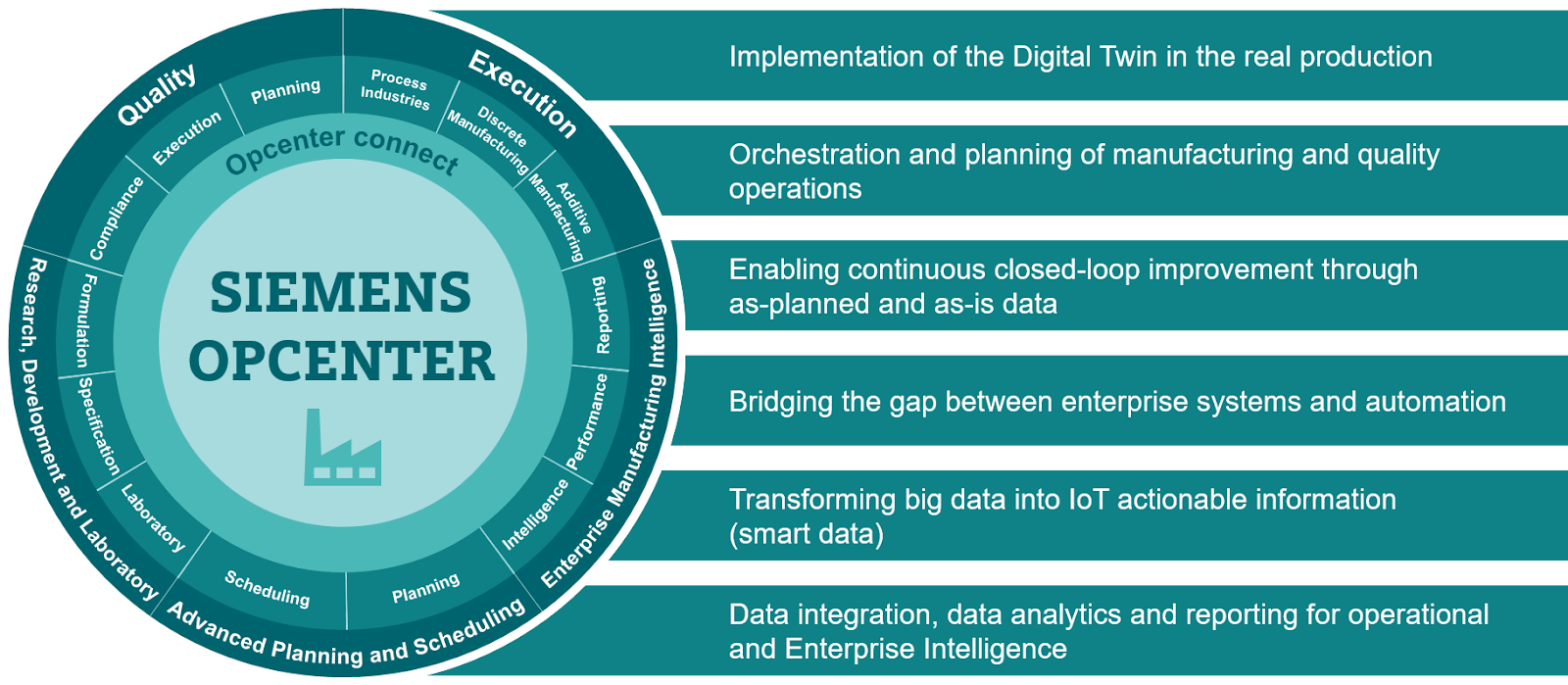
Siemens Opcenter for Aerospace Benefits:
- Descriptive analytics allow users to visualize and understand any potential manufacturing disruptions in real-time
- Equipment management increases machine availability and performance.
- Enables compliance, safety, and regulatory adherence through performance verification
Things to keep in mind:
Siemens Opcenter for aerospace is a powerful addition to the toolkit of any aerospace manufacturing engineer. The software primarily focuses on ingesting, aggregating, and contextualizing data from a manufacturing or assembly plant.
Its capabilities do not extend to prescriptive analytics, and to achieve this Siemens Opcenter for aerospace can be combined with operational intelligence platforms like Basetwo.
3. GE Digital Proficy Smart Factory (MES)
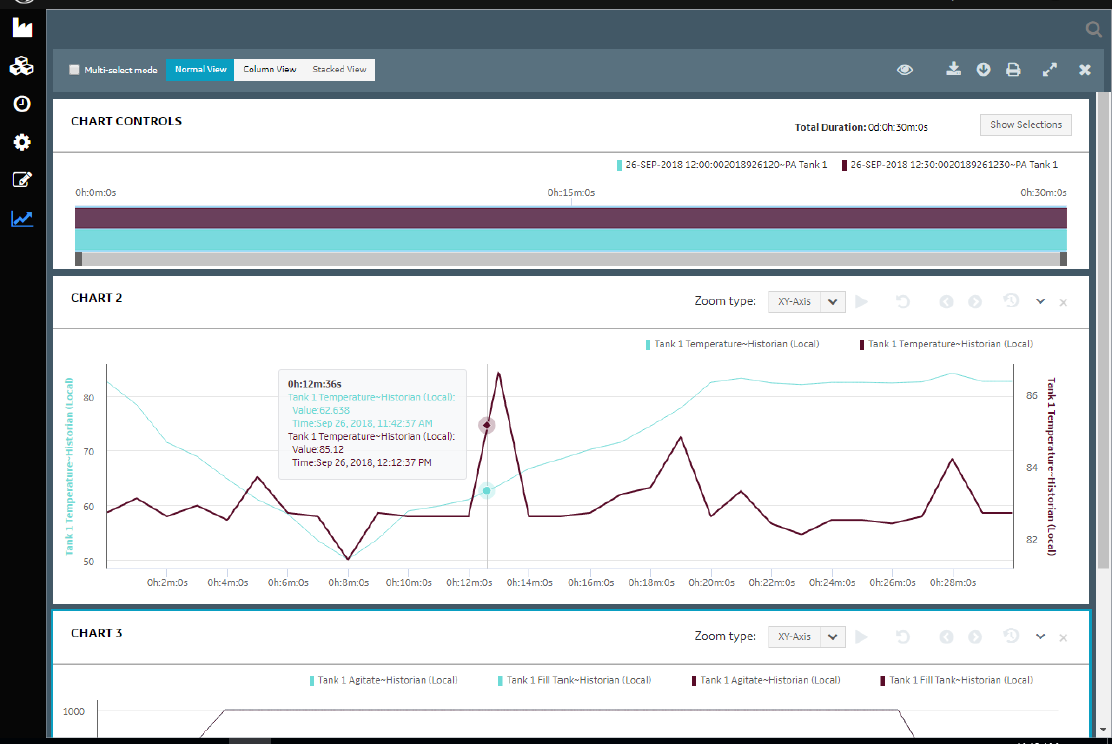
GE Digital Proficy Smart Factory (MES) is a suite of cloud-based and on-premises solutions, aimed at improving manufacturing operations.
The software is able to integrate with historical and real-time data sources such as PLCs, IoT devices, current ERP systems, and Excel.
Proficy Smart Factory (MES) tracks and monitors overall equipment efficiency (OEE) and other KPIs such as downtime, waste, and production counts by connecting with various data sources.
Proficy Smart Factory (MES) also supports compliance and regulatory initiatives by monitoring waste, scrap, and product recall events and costs.
The software also allows users to capture reasons for out-of-spec conditions enabling the resolution of quality issues faster.
Features:
- Comprehensive data integration for real-time monitoring and descriptive analytics
- KPI tracking and OEE monitoring
- Alarming
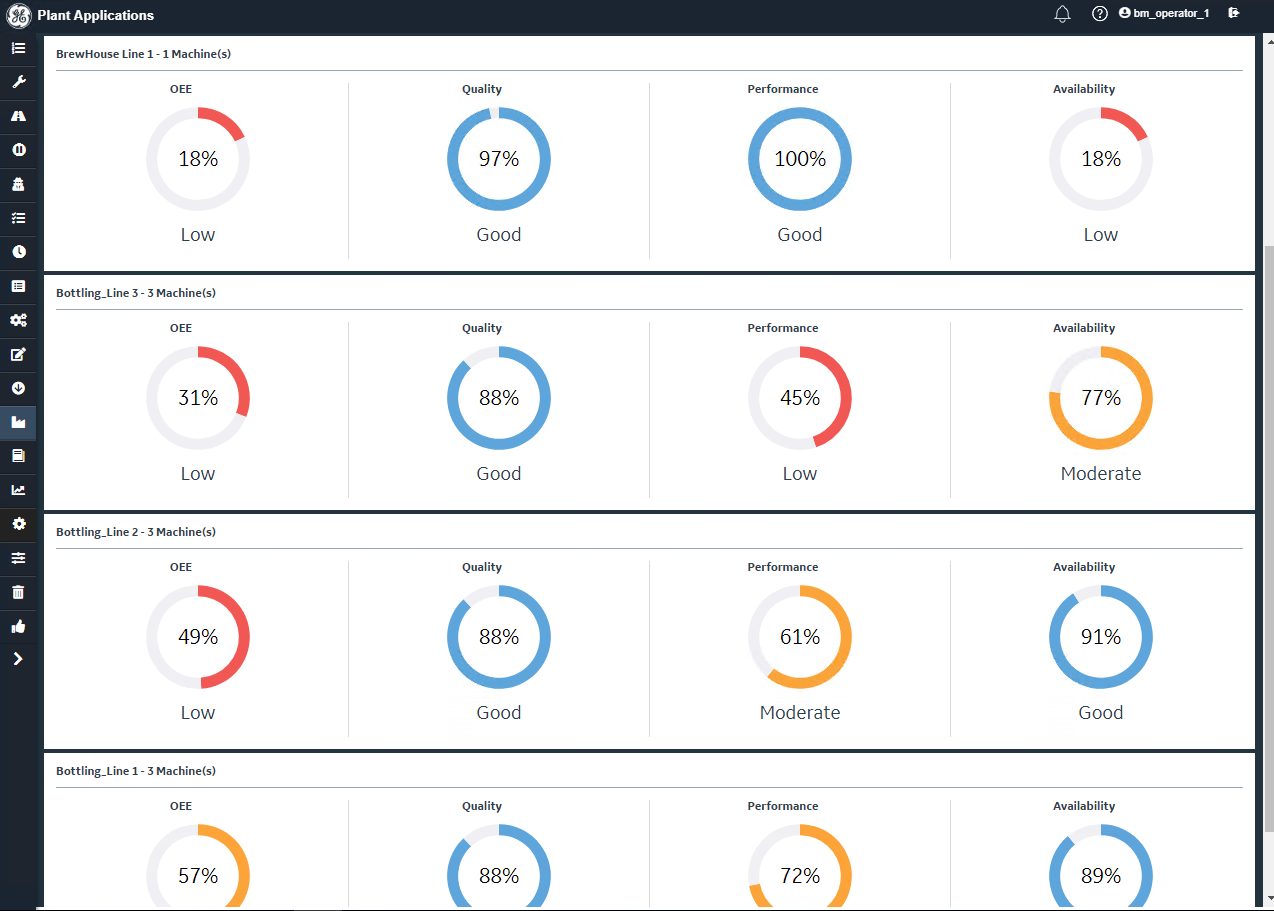
GE Digital Benefits:
- Comprehensive data integration and real-time monitoring.
- OEE and KPI monitoring allows better equipment management and less utility consumption.
- Provides compliance and regulatory support as well as capturing out-of-spec reasons to enable higher quality manufacturing.
Things to keep in mind:
GE Digital offers powerful record management and descriptive analytics functionality. The software allows users to capture reasons for out-of-spec conditions, enabling manufacturers to resolve quality issues faster in the future.
The ability to capture reasons for out-of-spec conditions and learn from past challenges can be further enhanced when coupled with operational intelligence platforms, like Basetwo.
By combining GE Digital Proficy Smart Factory (MES) with Basetwo, manufacturers have the ability to not only learn from their past challenges but further optimize operating procedures to ensure maximum KPIs under various plant constraints.
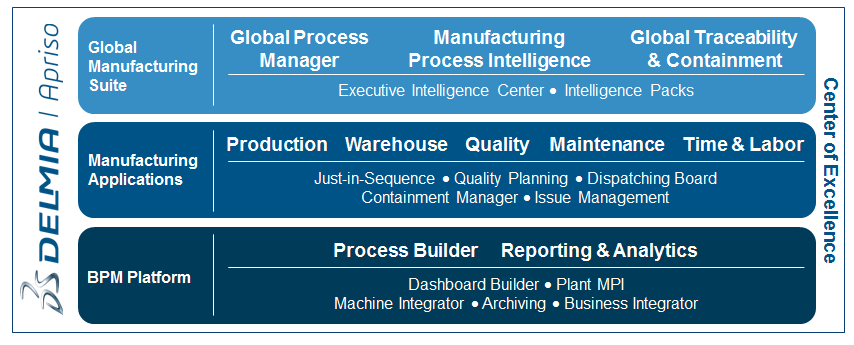
4. Dassault Systèmes DELMIA
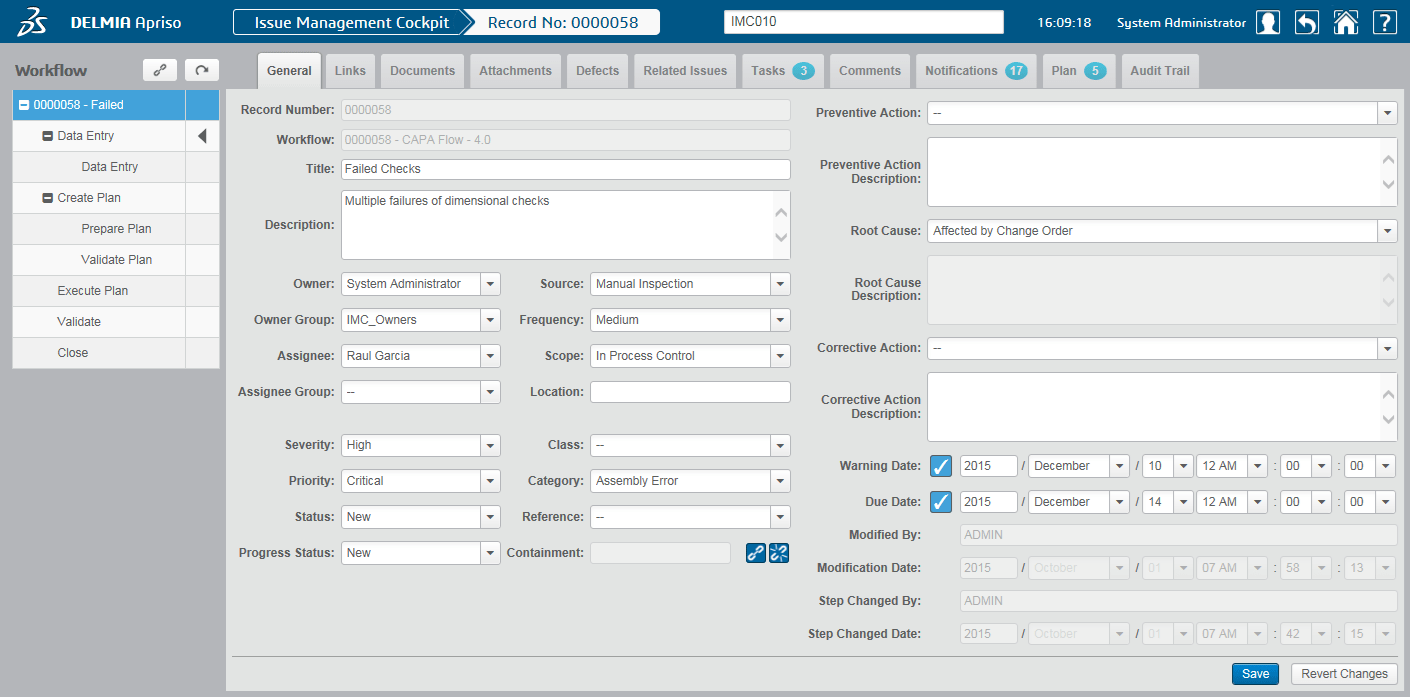
Dassault Systèmes DELMIA offers manufacturing engineers in the aerospace industry a suite of applications to manage all manufacturing processes through its Manufacturing Operations Management (MOM) and Manufacturing Execution System (MES) solutions.
DELMIA integrates with various real-time manufacturing data sources to provide manufacturing intelligence enabling enhanced manufacturing and quality control support.
DELMIA also offers real-time OEE monitoring, enabling maximum equipment performance.
It further supports quality management systems by providing access to all relevant data related to manufacturing.
Features:
- Real-time manufacturing data integration
- OEE monitoring
- Regulatory support
Benefits of Dassault Systèmes DELMIA:
- Real-time manufacturing data integration allows constant monitoring.
- Real-time OEE monitoring enables increased equipment availability.
- Tracks and documents the entire manufacturing process enabling better regulatory support.
Things to keep in mind:
DELMIA is a powerful aerospace manufacturing tool that allows real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and asset management.
This powerful platform does however have limitations.
The customization capabilities of DELMIA may lead to difficult deployment as it needs to be fully customized.
The optimization capability of DELMIA can also be improved when coupled with platforms like Basetwo which focuses on making process optimization easy and scalable for scientists and engineers.
Conclusion
The importance of manufacturing engineers implementing the correct software in the aerospace industry is paramount.
The various software options available have their distinct benefits and address specific demands in the aerospace industry.
As a standalone software option or as an addition to current platforms already being implemented, Basetwo is able to add value to any aerospace manufacturing operation.
Basetwo integrates seamlessly with existing software platforms and into existing workflows.
It is able to provide prescriptive analytics, generate process setpoints that maximize KPIs, and optimize operating procedures all through an easy to use, user-friendly platform. Basetwo, to date, has helped several Fortune 500 companies reduce material usage and operating costs by 40% while reducing energy consumption by 25%.

Are you interested in learning how Basetwo can help your aerospace manufacturing processes soar? Book your demo today!






.png)

.png)












.svg)